“Impact of Eastern Redcedar encroachment on water resources in the Nebraska Sandhills” #rxfire #nitrate #hydrology @gpfirescience @prairiefiresci
 Thursday, March 9, 2023 at 10:30AM
Thursday, March 9, 2023 at 10:30AM “Impact of Eastern Redcedar encroachment on water resources in the Nebraska Sandhills”
This article was published Oct. 24, 2022, in Science of the Total Environment. Access the article via the permanent web address (DOI). (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159696)
Highlights
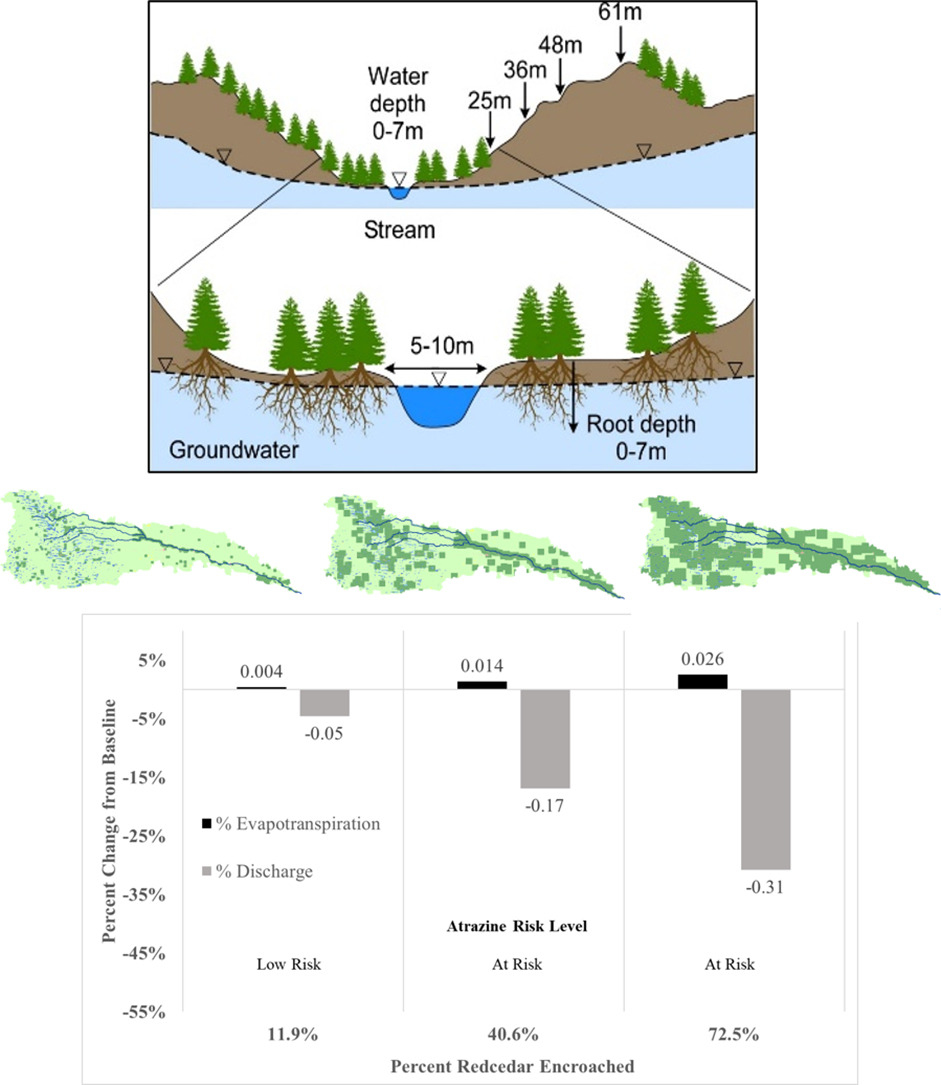
• Streamflow reduced by 46 % compared to historical flows for 100 % redcedar encroachment.
• Encroachment increases atrazine by 4 to 30 % compared to historical concentrations.
• Nitrate increases from 0.89–0.94 mg/L to 0.98–1.02 mg/L for 100 % encroachment.
Abstract
Worldwide, tree or shrub dominated woodlands have encroached into herbaceous dominated grasslands. While very few studies have evaluated the impact of Eastern Redcedar (redcedar) encroachment on the water budget, none have analyzed the impact on water quality.
In this study, we evaluated the impact of redcedar encroachment on the water budget in the Nebraska Sand Hills and how the decreased streamflow would increase nitrate and atrazine concentrations in the Platte River. We calibrated a Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT model) for streamflow, recharge, and evapotranspiration. Using a moving window with a dilate morphological filter, encroachment scenarios of 11.9 %, 16.1 %, 28.0 %, 40.6 %, 57.5 %, 72.5 % and 100 % were developed and simulated by the calibrated model.
At 11.9 % and 100 % encroachment, streamflow was reduced by 4.6 % and 45.5 %, respectively in the Upper Middle Loup River, a tributary to the Platte River. Percolation and deep aquifer recharge increased by 27 % and 26 % at 100 % encroachment. Streamflow in the Platte River, a major water source for Omaha and Lincoln, would decrease by 2.6 %, 5.5 % and 10.5 % for 28 %, 57.5 %, and 100 % encroachment of the Loup River watershed, respectively. This reduction in streamflow could increase nitrate and atrazine concentrations in the Platte River by 4 to 15 % and 4 to 30 %, respectively.
While the density of redcedar is minimal, it is important to manage their encroachment to prevent reductions in streamflow and potential increases in pollutant concentrations.
Keywords: Soil and Water Assessment Tool; Loup River Platte River; Atrazine; Baseflow-dominated watershed
Citation
Kishawi, Yaser, Aaron R. Mittelstet, Troy E. Gilmore, Dirac Twidwell, Tirthankar Roy, and Nawaraj Shrestha. "Impact of Eastern Redcedar encroachment on water resources in the Nebraska Sandhills." Science of The Total Environment 858 (2023): 159696.
